Overview of the Japanese Education System
The Japanese Education System
- Overview of the Japanese Education System
- Types of Higher Education Institutions
- Higher Education Qualifications
- Admission to Higher Education Institution
- Quality Assurance System
- Learning Assessment
Overview of the Education System
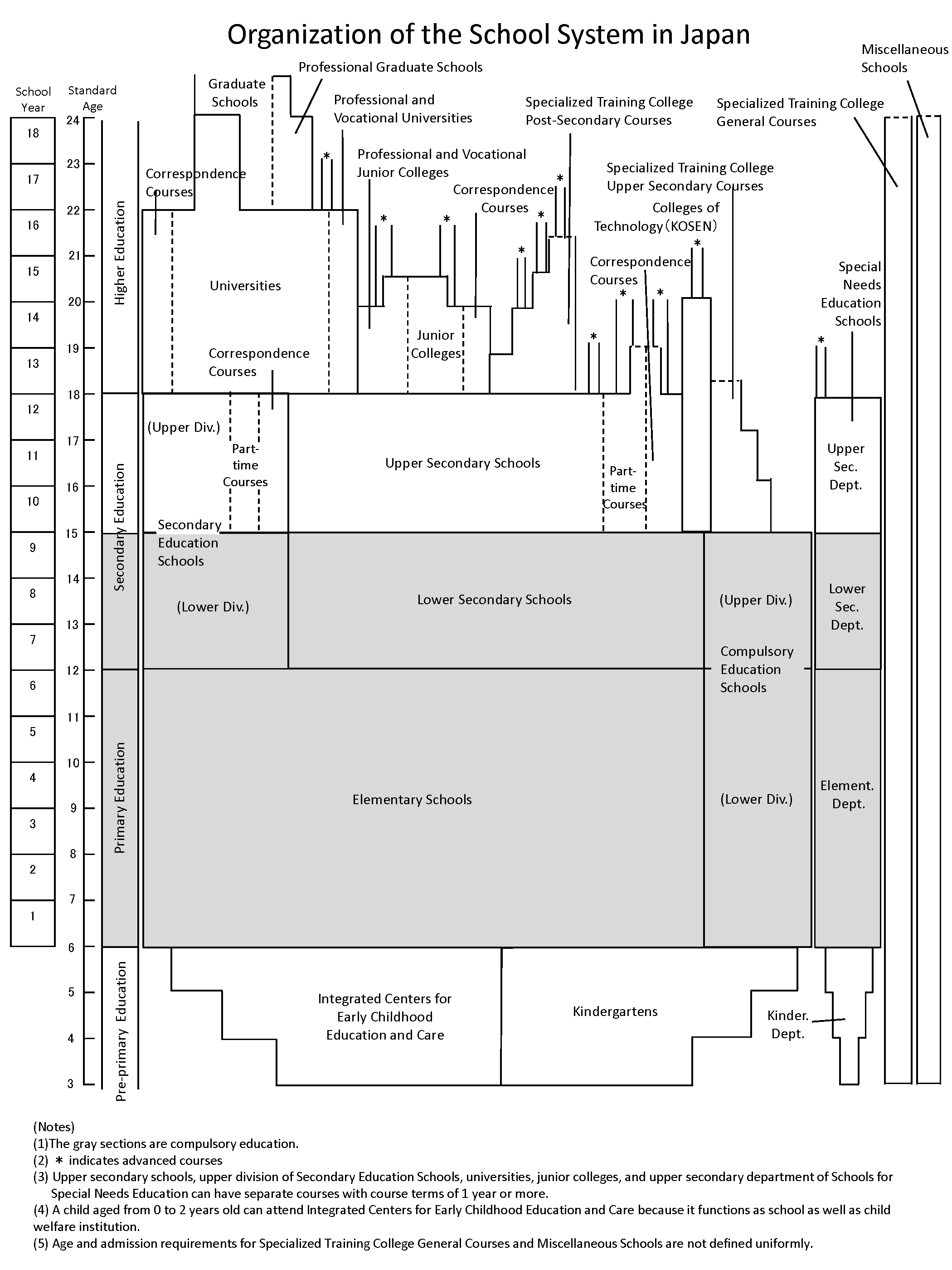
The Japanese educational system starts with pre-school education, followed by 6 years of elementary education, then 6 years of secondary education (3 years of lower secondary and 3 years of upper secondary education), which leads to a wide range of higher education. The 9 years of elementary and lower secondary education cover compulsory education.
There are kindergartens (幼稚園 yochien), day care centers (保育所 hoikusho), and “centers for early childhood education and care” (認定こども園 nintei-kodomo-en) for pre-school education. As for elementary and secondary education, typical educational institutions include elementary schools (小学校 shogakko) for elementary education and lower secondary schools (中学校 chugakko) and upper secondary schools (高等学校 kotogakko) for secondary education. There are also schools for special needs education (特別支援学校 tokubetsu-shien-gakko) [departments of kindergarten, elementary, lower secondary, and upper secondary] for children and students with disabilities.
In addition, in 1998, it became possible to establish 6-year Secondary Education Schools (中等教育学校 chuto-kyoiku-gakko) which combine lower and upper secondary education, and in 2016, it became possible to establish Compulsory Education Schools (義務教育学校 gimu-kyoiku-gakko) which combine elementary and lower secondary education.
For upper division of Secondary Education Schools and upper secondary schools, there are also schools that offer part-time courses (定時制 teiji-sei) in the evening or at other specific times and periods, correspondence courses (通信制 tsushin-sei) that offer distance education, and 高等専修学校 koto-senshu-gakko which is Upper Secondary Courses of Specialized Training Colleges (専修学校高等課程 senshu-gakko-koto-katei).
Types of higher education institutions (HEIs), higher education qualifications, and admissions are described in the following sections.
Organization of the School System in Japan
Academic Calendar
Governed by law, the academic year for elementary and secondary education institutions and Colleges of Technology (KOSEN) starts on April 1 and ends on March 31. At universities and Specialized Training Colleges, rectors or presidents determine the beginning and end of the academic year for their institutions. At upper secondary schools, upper secondary department of schools for special needs education, and universities, matriculation and graduation of students may take place in the middle of an academic year according to the division of academic term of each institution.
Many universities in Japan use a semester system (first semester from April to September, and second semester from October to March), but there are also some universities that use trimester or quarter systems.
Statistics of Higher Education
(As of May 1, 2024)
Number of Higher Education Institutions
| National | Public | Private | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| University*1 | 86 | 103 | 624 | 813 |
| Junior College | --- | 15 | 282 | 297 |
| College of Technology (KOSEN) | 51 | 3 | 4 | 58 |
| Professional Training College (Specialized Training College which offers Post-Secondary Course)*2 | 8 | 176 | 2,492 | 2,676 |
| Education institutions operated by government ministries and agencies*3 | 3 | --- | --- | 3 |
Number of Student Enrolment in Higher Education
| National | Public | Private | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| University*1 | 603,967 | 168,072 | 2,177,756 | 2,949,795 |
| Junior College | --- | 4,921 | 73,374 | 78,295 |
| College of Technology (KOSEN) | 50,859 | 3,762 | 1,721 | 56,342 |
| Post-Secondary Course of Professional Training College*2 | 215 | 20,549 | 537,491 | 558,255 |
Number of Full-time Faculty and Staff in Higher Education
| National | Public | Private | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| University*1 | Full-time Faculty | 63,823 | 14,854 | 113,854 | 192,531 |
| Full-time Staff | 91,985 | 20,701 | 155,819 | 268,505 | |
| Junior College | Full-time Faculty | --- | 385 | 5,852 | 6,237 |
| Full-time Staff | --- | 165 | 3,224 | 3,389 | |
| College of Technology (KOSEN) | Full-time Faculty | 3,506 | 276 | 140 | 3,922 |
| Full-time Staff | 2,627 | 105 | 66 | 2,798 | |
| Post-Secondary Course of Professional Training College*2 | Full-time Faculty | 75 | 2,554 | 33,077 | 35,706 |
<Reference> MEXT, School Basic Survey Results [Japanese only], etc.
*1 Includes graduate schools.
*2 33 prefectural colleges of agriculture (農業大学校) are included in 'Public'.
*3 Only the institutions defined by the "Guideline for the Recognition of Higher Education Qualifications - Asia-Pacific Regional Convention on the Recognition of Qualifications in Higher Education" (MEXT, 2019) are included. There is no published statistical data on the numbers of student enrolment, full-time faculty and staff.
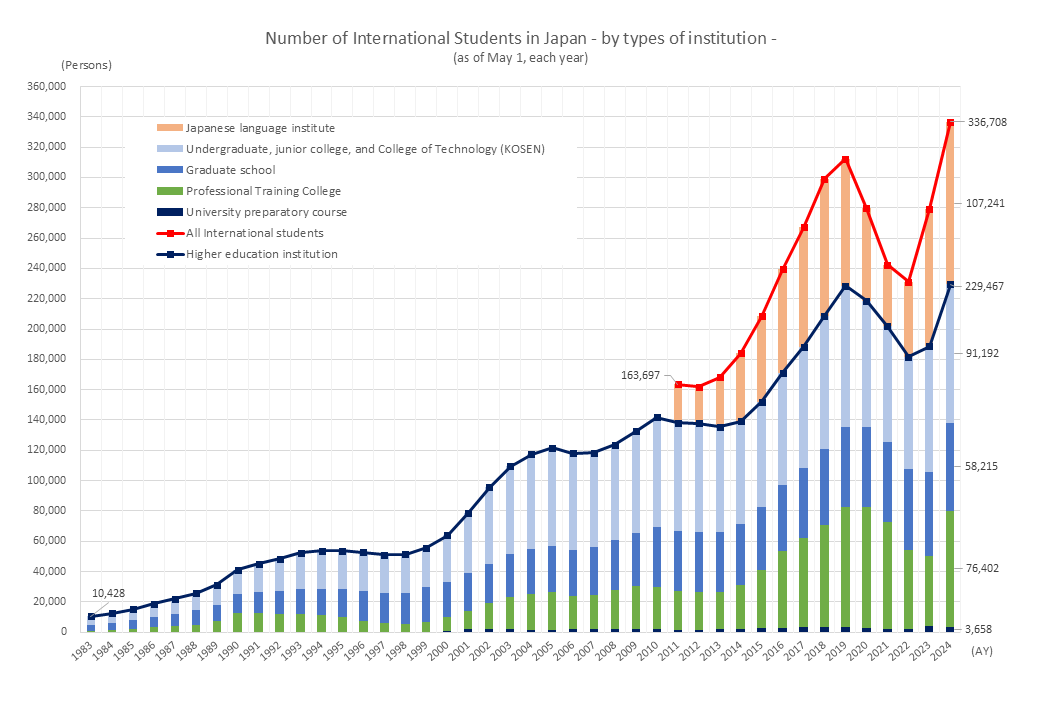
Number of International Students in Japan
Reference
JASSO (2025) Result of International Student Survey in Japan, 2024
This graph was created by NIC-Japan based on the JASSO survey results.
Number of Japanese Students Studying Abroad
Major Laws and Regulations Pertaining to Higher Education
For the laws and regulations listed below, English translation is avialable for Basic Act on Education only. Please also note that only the original Japanese texts have legal effect, and the English translations are to be used solely as reference materials.
- Basic Act on Education (Act No.120 of 2006 amended Act No.25 of 1947 in its entirety.)
- School Education Act (Act No.26 of 1947)
- Order for Enforcement of
the School Education Act (Cabinet Order No.340 of 1953) - Enforcement Regulation of
the School Education Act (Ordinance of the Ministry of Education No.11 of 1947) - Degree Regulations (Ordinance of the Ministry of Education No.9 of 1953)
- Rules on granting the titles of Diploma and Advanced Diploma to graduates of Post-secondary Courses of Specialized Training Colleges (Public Notice of the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture No.84 of June 21, 1994)
Links to Standards for the Establishment of each type of higher education institutions are listed on the Quality Assurance System page.