Admission to Higher Education Institution
The Japanese Education System
- Overview of the Japanese Education System
- Types of Higher Education Institutions
- Higher Education Qualifications
- Admission to Higher Education Institution
- Quality Assurance System
- Learning Assessment
Admission Qualifications and Pathways in Higher Education
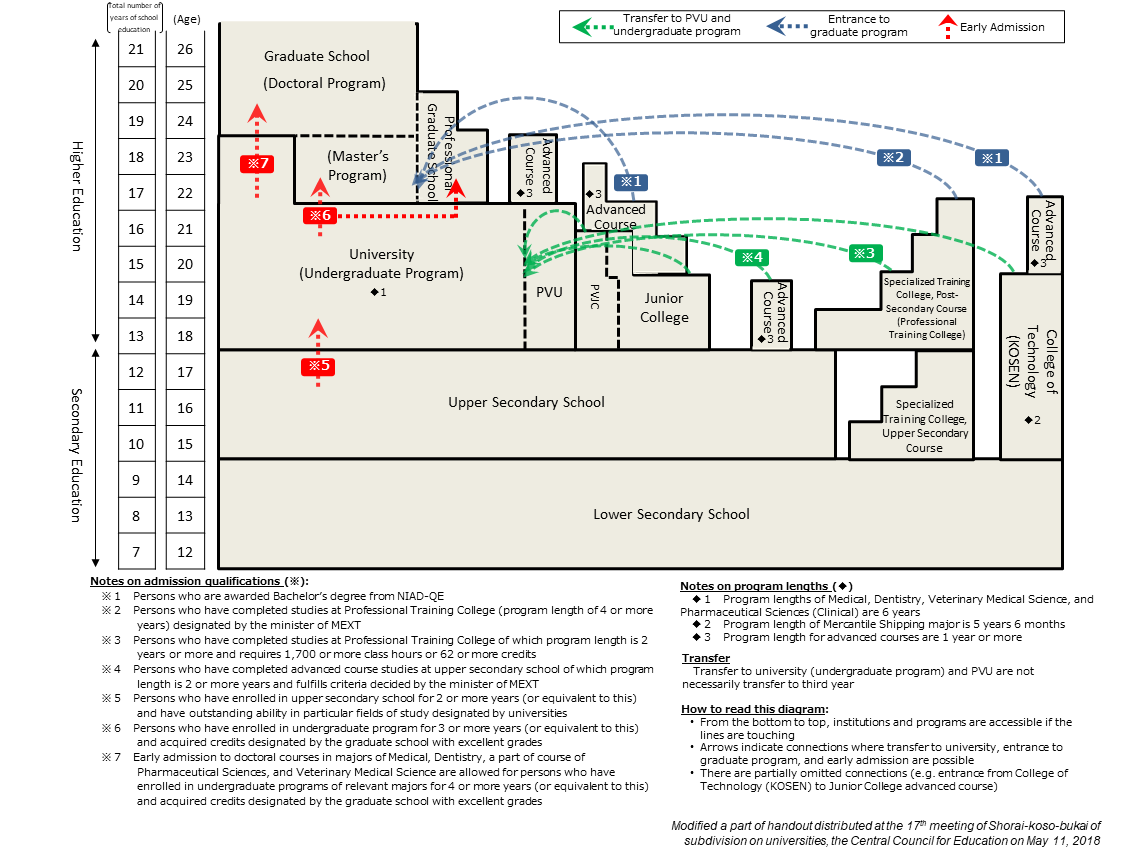
To enroll in an HEI, applicants must fulfil admission qualifications in accordance with the School Education Act and its Enforcement Regulations, and pass examinations or other selection procedures determined by each institution.
There are also cases in which individual institutions set their own application requirements in addition to those of the law.
Higher Education Pathways
Admission Eligibility
Admission to University
Admission to University (Undergraduate Program), Professional and Vocational University (PVU), Junior College, and Professional and Vocational Junior College (PVJC)
In principle, under the law, persons who have completed 12 years of school education or designated school education (primary and secondary education) are eligible to enroll in a university (undergraduate program), PVU, junior college and PVJC. Persons who have received 12 years of school education outside Japan are treated equally.
Alternatively, persons who have passed Upper Secondary School Equivalency Examination (高等学校卒業程度認定試験 kotogakko-sotsugyo-teido-nintei-shiken, the exam which certifies equivalency of one’s scholastic competency to completion of 12 years of school education), or have a certificate to enroll in foreign universities, International Baccalaureate, Abitur, Baccalaureate, and General Certificate of Education Advanced Level are also eligible for university admission in Japan. There are also cases in which each institution accepts applicants based on its own admission qualification assessment.
▶See MEXT website for details on admission qualifications [Japanese] [English]
▶See here for admission eligibility of those who have graduated from a foreign or international school
[Major Laws and Regulations Pertaining to Admission Qualifications for Universities]
- Article 90, School Education Act
- Article 150, Enforcement Regulation of the School Education Act
- Public Notice of the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture No.153 of 1981 (A person equivalent to those who have completed a 12-year school education course in a foreign country under the provisions of Article 150, item (i) of the Enforcement Regulation of the School Education Act) [excerpt]
- Public Notice of the Ministry of Education No.47 of 1948 (A person who is deemed as having the academic ability equivalent to or greater than graduates of upper secondary schools with regard to university admission, prescribed in Article 150, item (iv) of the Enforcement Regulation of the School Education Act) [excerpt]
- Public Notice of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology No.75 of 2016 (Standards for courses of foreign schools corresponding to upper secondary schools that a person who has completed the course is deemed as having academic abilities equivalent to or greater than graduates of upper secondary schools with regard to university admission) [excerpt]
- Public Notice of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology No.177 of 2016 (Notification to designate courses of foreign schools corresponding to upper secondary schools that a person who has completed the course is deemed as having the academic ability equivalent to or greater than graduates of upper secondary schools with regard to university admission) [List of Courses of Foreign Schools Corresponding to Upper Secondary Schools Designated by the Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (English)]
Early Admission
The system of early admission allows students to enroll in a university at an earlier stage than the above standard. It aims to develop further the talents of persons with outstanding ability in a particular field from the viewpoint of promoting education that corresponds to individual abilities and qualities. Persons who are considered to have outstanding ability in particular fields of study, designated by each university, and have attended upper secondary school for 2 years or longer are eligible for early admissions. The universities must also fulfill legal requirements in order to implement the system.
Since students who are granted early admission will need to drop out of upper secondary school to enroll in a university, in response to this situation, the Upper Secondary School Equivalency Certification System (高等学校卒業程度認定審査 kotogakko-sotsugyo-teido-nintei-shinsa) [Japanese only] was introduced on April 1, 2022. Under this system, the Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology certifies that a student who has entered a university by early admission has academic abilities equivalent to or greater than graduates of upper secondary schools based on their learning outcomes or equivalent from upper secondary school and university.
▶See here for details [Japanese only]
Transfer to University (Undergraduate Program) and Professional and Vocational University (PVU)
Transfer refers to the admission when a person who has completed education at an institution enters another type of institution. Transferred students start from the middle of the course and are exempted from a part of the curriculum. Persons who have fulfilled one of the following legal requirements can transfer to a university (undergraduate program) or PVU:
(1) Graduation from junior college (also applicable for junior colleges overseas),
(2) Graduation from Professional and Vocational Junior College,
(3) Graduation from College of Technology (KOSEN),
(4) Completion of Post-Secondary Course at Professional Training College (program length must be 2 years or longer, with 1700 credit hours or more or 62 or more credits),
(5) Completion of certain upper secondary school Advanced Courses, or
(6) Graduation from a Japan branch campus of foreign university, which is designated as being equivalent to Japanese junior college by the Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology.
▶See MEXT website for details on transfer admissions [Japanese] [English]
Admission to Graduate School and Professional Graduate School
Admission to graduate school and Professional Graduate School is eligible to persons who have graduated from a university (undergraduate program), have graduated from a Professional and Vocational University, have received bachelor’s degree from NIAD-QE, or have completed 16 years of school education (18 years for medicine, dentistry, pharmaceutical sciences, and veterinary medical science majors). There are also cases in which each institution accepts applicants based on its own admission qualification assessment.
▶See MEXT website for details of admission eligibility of master’s and professional degree programs [Japanese] [English]
▶See MEXT website for details of admission eligibility of doctoral programs [Japanese] [English]
[Major Laws and Regulations Pertaining to Admission Qualifications for Graduate Schools]
- Article 102, School Education Act
- Article 155, paragraph (1) and Article 156, Enforcement Regulation of the School Education Act
- Public Notice of the Ministry of Education No.5 of 1953 (A person who is deemed as having the academic ability equivalent to or greater than graduates of universities with regard to admission to graduate school and advanced course of a university under the provisions of Article 155, paragraph (1), item (vi) of the Enforcement Regulation of the School Education Act) [excerpt]
- Public Notice of the Ministry of Education No.39 of 1955 (A person who is deemed as having the academic ability equivalent to or greater than graduates of universities with regard to admission to doctoral program or advanced course, etc. majoring in medicine, under the provisions of Article 155, paragraph (1), item (vi) of the Enforcement Regulation of the School Education Act) [excerpt]
- Public Notice of the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture No.118 of 1989 (A person who is deemed as having the academic ability equivalent to a person with a master's degree with regard to graduate school admission under the provisions of Article 156, item (vi) of the Enforcement Regulation of the School Education Act) [excerpt]
Early Admission
The system of early admission allows students to enroll in a graduate school at an earlier stage than the above standard. It aims to develop further the talents of persons with outstanding ability in a particular field from the viewpoint of promoting education that corresponds to individual abilities and qualities. Students who have attended university (undergraduate program) for 3 years or longer and earned required credits with excellent grades are eligible for early admissions. The graduate schools must also fulfill legal requirements in order to implement the system.
▶See here for details [Japanese only]
Admission to College of Technology (KOSEN)
College of Technology (KOSEN) programs begin from the level of upper secondary education. Therefore, admission eligibility is the same as those of upper secondary schools, i.e. completion of lower secondary education in the Japanese school system or 9 years of school education in a non-Japanese school system.
▶See here for details [Japanese only]
[Major Laws and Regulations Pertaining to Admission Qualifications for Colleges of Technology (KOSEN)]
- Article 118, School Education Act
- Article 179, Enforcement Regulation of the School Education Act (Mutatis mutandis application of Article 95)
- Public Notice of the Ministry of Education No.58 of 1948 (A person who is deemed as having the academic ability equivalent to or greater than graduates of lower secondary schools with regard to upper secondary school admission prescribed in Article 63 of the Enforcement Regulation of the School Education Act)
Admission to Professional Training College
Admission eligibility to Professional Training College differs depending on the type of the program. As for Post-secondary Courses, the law stipulates that persons who have completed 12 years of school education (primary and secondary education) are, in principle, eligible to enroll, as is the case with university (undergraduate program). Persons who have received 12 years of school education outside Japan are treated equally.
Persons who passed Upper Secondary School Equivalency Examination, or have a certificate to enroll in foreign universities such as International Baccalaureate or Abitur are also eligible for admission to Post-secondary Course of Professional Training College. There are also cases in which each institution accepts applicants based on its own admission qualification assessment.
▶See here for details [Japanese only]
[Major Laws and Regulations Pertaining to Admission Qualifications for Post-Secondary Courses of Specialized Training College]
- Article 125, paragraph (3), School Education Act
- Article 150 and Article 183, Enforcement Regulation of the School Education Act
- Public Notice of the Ministry of Education No.47 of 1948 (A person who is deemed as having the academic ability equivalent to or greater than graduates of upper secondary schools with regard to university admission prescribed in Article 150, item (iv) of the Enforcement Regulation of the School Education Act) [excerpt]
- Public Notice of the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture No.153 of 1981 (A person equivalent to those who have completed a 12-year school education course in a foreign country under the provisions of Article 150, item (i) of the Enforcement Regulation of the School Education Act) [excerpt]
Admission to Educational Institutions Operated by Government Ministries and Agencies
Admission to educational institutions operated by government ministries and agencies depends on the institution. In some cases, they are regulated by legislation and instruction of the operating government ministry.
Entrance Examinations
In principle, Japanese HEIs select students based on each institution’s own procedures established in line with its admission policy.
University Entrance Examinations
University (Undergraduate Program), Professional and Vocational University (PVU), Junior College, and Professional and Vocational Junior College (PVJC)
Entrance examinations for university (undergraduate program), PVU, junior college, and PVJC are conducted based on "the Guidelines for University Entrance Examinations" [Japanese only] stipulated and renewed every academic year by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology. The Guideline contents include selection methods, timing of selection, etc.
Selection processes vary from institution to institution: considering the "Common Test for University Admissions" (see explanation below) scores, conducting original scholastic exams and interviews, combining document screening and interview, to name a few. In addition, some institutions employ special procedures for non-Japanese applicants.
The Common Test for University Admissions (大学入学共通テスト Daigaku-nyugaku-kyotsu-tesuto)
The Common Test for University Admissions is a standardized exam designed for students who are graduating or have already graduated from upper secondary school and willing to enter a university (undergraduate program). It takes place simultaneously throughout the country in mid-January every year. It is an option for universities take scores from this exam into consideration, and the universities that use its scores administer the Test in collaboration with the National Center for University Entrance Examinations. Multiple choice written exams (and listening comprehension for English) are administered for 30 subjects in six subject areas (i.e. Japanese Language, Geography and History, Civics, Mathematics, Science, and Foreign Languages). It is up to each university to specify the subject areas and subjects and how to use the scores for their admission procedures, whether it is a requirement or just a supplementary resource.
The Test has been implemented since AY2021, replacing the National Center Test, which had been implemented from AY 1990 through AY2020.
▶See here for details of the Common Test for University Admissions [Japanese only]
Examination for Japanese University Admission for International Students (EJU)
The EJU is an examination for international students planning to study at a Japanese university (undergraduate program) to measure Japanese language proficiency and basic academic abilities needed to study at a Japanese HEI.
EJU is administered through Japan Student Services Organization (JASSO) and it takes place twice a year, in June and November, both in Japan and overseas. The exam can be taken in Japanese or English, and the subjects include Japanese as a Foreign Language, Science (Physics, Chemistry, and Biology), Japan and the World, and Mathematics. It is up to each university to specify the subjects and language of the exam the examinees take. Many universities use EJU scores as a reference resource in the special selection for international applicants.
▶See here for details of the EJU
Graduate School and Professional Graduate School
Entrance examinations for graduate school and Professional Graduate School are conducted based on the Guidelines for Graduate School Entrance Examinations stipulated by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology in 2008. Selection procedures vary from institution to institution; for example, applicants are judged comprehensively by combination of document screening, scholastic test, interview, etc. When a student is continuing studies from undergraduate program to the graduate school in the same university, s/he can take recommendation-based entrance exam, which gives exemption from part of the selection procedures. Recently, the number of graduate schools introducing AO exams (exams conducted independently by an Admissions Office) are increasing. There are also cases in which non-Japanese applicants undergo special selection procedures, and such cases may use EJU scores as a reference.
College of Technology (KOSEN) Entrance Examinations
Entrance examination for College of Technology (KOSEN) is either scholastic test or recommendation-based entrance exam for all national, public, and private colleges. In addition to the above, some Colleges of Technology (KOSEN) also conduct AO exams and special selection for Japanese students who received secondary education abroad. All 51 national Colleges of Technology (KOSEN) use the same examination for scholastic testing which takes place simultaneously throughout the country. There are also cases in which non-Japanese applicants undergo special selection procedures, and such cases may use EJU scores as a reference.
Professional Training College Entrance Examinations
Entrance examination for Professional Training College differs from institution to institution. The exams vary depending on the characteristics of the study areas and departments. There are also cases in which non-Japanese applicants undergo special selection procedures, and such cases may use EJU scores as a reference.
Educational Institution Operated by Government Ministries and Agencies Entrance Examinations
Each educational institution operated by a government ministry or agency decides its own admission procedures. They are written exams, recommendation-based entrance exams, and special selection for Japanese students who received secondary education abroad, to name a few. Types of exams also vary from document screening, scholastic test, interview, to short essay, etc.