Japanese Educational Qualifications Framework
The Japanese Education System
- Overview of the Japanese Education System
- Types of Higher Education Institutions
- Higher Education Qualifications
- Admission to Higher Education Institution
- Quality Assurance System
- Japanese Educational Qualifications Framework
Japanese Educational Qualifications Framework
This Educational Qualifications Framework is an official guide to qualifications that can be obtained in the Japanese school system. Through the development by NIAD-QE, it was endorsed by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), Japan in 2025.
【Aim】
This qualifications framework aims to increase the transparency and social understanding of Japanese educational qualifications at home and abroad and ensure qualification holders who wish to pursue higher education or find employment will not be disadvantaged. It was formulated through mapping based on legal grounds such as course completion requirements and admission eligibility. Qualifications at the same level are not considered “homogeneous,” but “equivalent” or “comparable.”
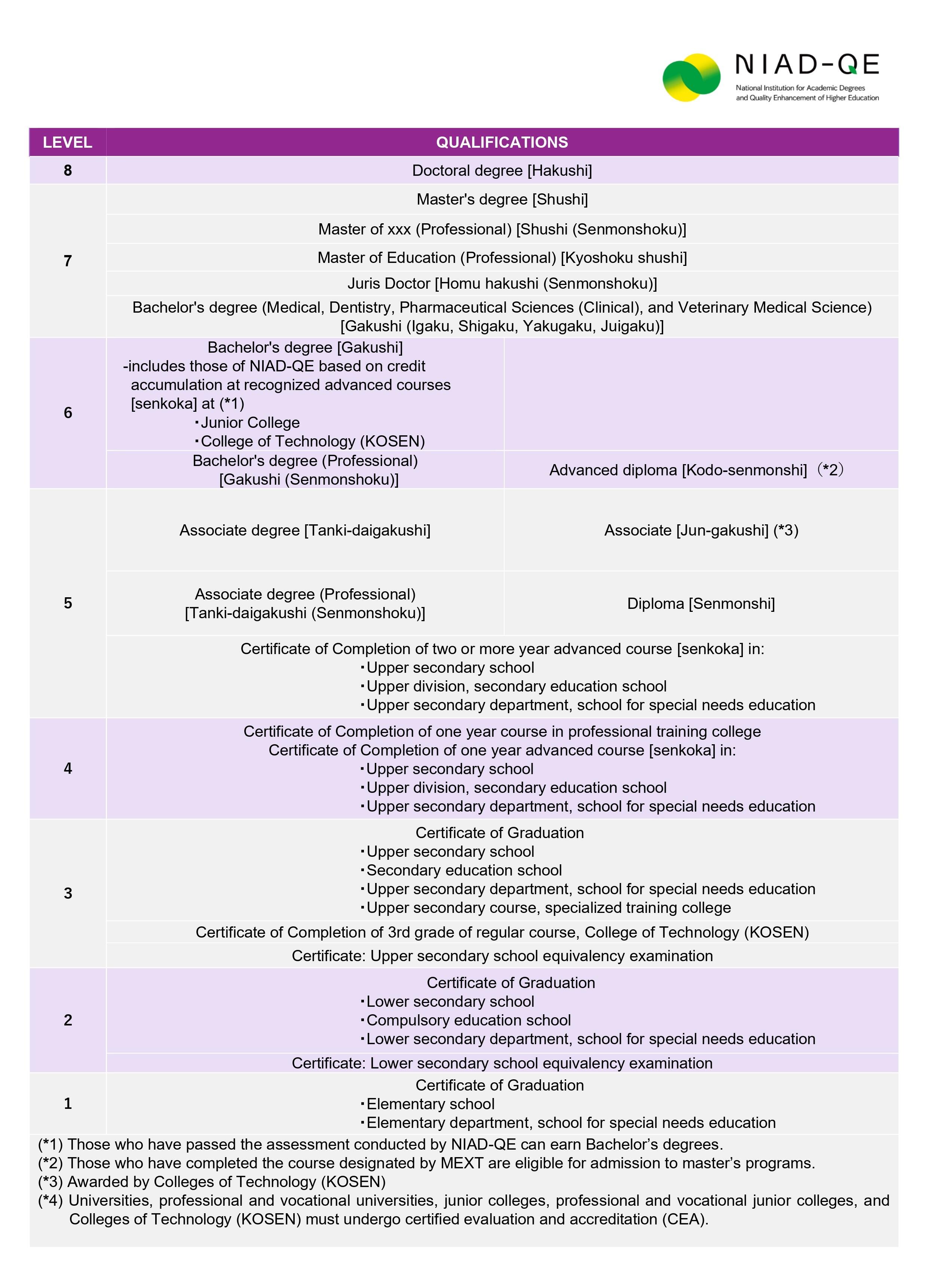
Japanese Educational Qualifications Framework (PDF)
Learn More
(*1) Those who have passed the assessment conducted by NIAD-QE can earn Bachelor’s degrees.
(*2) Those who have completed the course designated by MEXT are eligible for admission to master’s programs.
(*3) Awarded by Colleges of Technology (KOSEN).
(*4) Universities, professional and vocational universities, junior colleges, professional and vocational junior colleges, and Colleges of Technology (KOSEN) must undergo certified evaluation and accreditation (CEA).
Remarks
Doctoral degree [Hakushi]
・A degree generally awarded when completing a graduate school’s doctoral degree program.
・Awarding institutions: Universities with graduate schools and National Institution for Academic Degrees and Quality Enhancement of Higher Education (NIAD-QE)
・There are two types of doctoral degree programs: five-year integrated programs and those divided into two parts—the first two-year master’s level and the second three-year doctoral level.
・In addition to the required years of study and credit hours for completing the doctoral degree program, students must receive the necessary research guidance and pass the dissertation defense and an examination.
・The university may also award a doctoral degree to those who have passed the examination of the doctoral dissertation conducted by the graduate school and are confirmed to have academic abilities equivalent to those who have completed a doctoral course at the graduate school (so-called doctoral degree by thesis only), as determined by the university.
・NIAD-QE awards doctoral degrees to those who have completed courses at educational institutions in Japan operated by government ministries and agencies that are recognized by NIAD-QE as offering a level of education equivalent to a doctoral course, and who have passed the assessment conducted by NIAD-QE.
Master’s degree [Shushi]
・A degree generally awarded when completing a graduate school’s master’s program, the first (two-year master’s) level of a doctoral degree program.
・Awarding institutions: Universities with graduate schools and NIAD-QE
・The standard duration of a master’s program is two years, however, if the prescribed conditions are met, such as providing education primarily for those with work experience, the standard duration of study may be set at between one and less than two years (Article 3, Paragraph 3 of the Standards for the Establishment of Graduate Schools). In such cases, the requirement for completion (minimum enrollment period) extends beyond the standard duration of study.
・In addition to the number of years of study and the number of credits earned, the requirements for completion of a master’s degree program include receiving the necessary research guidance, reviewing a master thesis or results of research on a specific topic, and passing an examination. For the requirements for completing the first term of a doctoral program that is divided into two terms, passing the Qualifying Examination (an examination and review conducted by the graduate program) can substitute for passing the master’s thesis or the examination of research results on a specific topic.
・NIAD-QE awards master’s degrees to those who have completed courses at educational institutions in Japan operated by government ministries and agencies that are recognized by NIAD-QE as offering a level of education equivalent to a master’s degree and who have passed the assessment conducted by NIAD-QE.
Master of xxx (Professional) [Shushi (Senmonshoku)]
・A degree awarded when completing a professional graduate school’s program (except programs of graduate law school and graduate education school).
・Awarding institutions: Universities with graduate schools
Master of Education (Professional) [Kyoshoku shushi]
・A degree awarded when completing a professional graduate education school
・Awarding institutions: Universities with graduate schools
Juris Doctor [Homu hakushi (Senmonshoku)]
・A degree awarded when completing a professional graduate law school
・Awarding institutions: Universities with graduate schools
Bachelor’s degree (Medical, Dentistry, Pharmaceutical Sciences (Clinical), and Veterinary Medical Science) [Gakushi (Igaku, Shigaku, Yakugaku, Juigaku)]
・Awarding institutions: Universities
・Graduation from a 6-year undergraduate program in medicine, dentistry, pharmacy, or veterinary science alone does not make this equivalent to a master’s program, nor does it qualify for direct admission to a doctoral program (3-year term). However, it may be possible to enter the doctoral program (3-year term) from such a 6-year undergraduate program through an individual admission eligibility screening (Article 156, Item 7 of the Regulations for Enforcement of the School Education Act) at the receiving institution.
・Graduates of 6-year undergraduate programs in medicine, dentistry, pharmacy, and veterinary medicine are eligible for admission to 4-year doctoral programs in medicine, dentistry, pharmacy, and veterinary medicine.
Bachelor’s degree [Gakushi]
・Awarding institutions: Universities and NIAD-QE
・NIAD-QE awards bachelor’s degrees on:
1) Those who have completed a certain level of study at higher education institutions such as a junior college or college of technology (KOSEN), earned the required credits through the credited auditor system or advanced courses recognized by NIAD-QE, and who, based on NIAD-QE’s assessment, are deemed to possess academic abilities equivalent to those of university graduates.
2) Those who have completed courses at educational institutions in Japan operated by government ministries and agencies that are recognized by NIAD-QE as providing a level of education equivalent to a bachelor’s degree, and who have passed the assessment conducted by NIAD-QE.
Bachelor’s degree (Professional) [Gakushi (Senmonshoku)]
・Awarding Institutions: Professional and vocational universities
Advanced diploma [Kodosenmonshi]
・A title awarded when completing specialized training college offering post-secondary courses designated by the Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology.
・Awarding institutions: Specialized training college offering post-secondary courses.
・Specialized training colleges offering post-secondary courses are eligible for admission to master’s degree programs upon completing a course that meets the prescribed requirements (at least four years of study, a total of 3,400 or more class hours, over 124 credits, etc.) and is designated by the Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology. Additionally, those who complete a program designated by the Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology are awarded an advanced diploma.
Associate degree [Tankidaigakushi]
・Awarding institutions: Junior colleges (*)
*Junior college: A university with 2 or 3 years of study.
Associate degree (Professional) [Tankidaigakushi (Senmonshoku)]
・Awarding institutions: Professional and vocational junior colleges and, professional and vocational universities.
・For professional and vocational universities, an associate degree (professional) is awarded to those who have completed the first term (only in the case of professional and vocational universities that offer both the first and second terms).
Associate [Jungakushi]
・A title awarded when completing College of Technology (KOSEN).
・Awarding Institutions: College of Technology (KOSEN).
・Colleges of Technology (KOSEN) are five-year higher education institutions that start at the upper secondary education (level 3).
Diploma [Senmonshi]
・A title awarded when completing specialized training college offering post-secondary courses designated by the Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology.
・Awarding institutions: Specialized training college offering post-secondary courses.
・For special training college courses, those who complete a course that meets the prescribed requirements (at least two years of study, a total of 1,700 or more class hours, or 62 or more credits, etc.) are eligible to transfer to a university. Additionally, those who complete a program designated by the Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology are awarded a diploma.
Certificate of Completion: Two or more year advanced course, upper secondary school
・While the duration of study for the advanced course at the upper secondary school is at least one year, those who complete two or more years and meet the standards specified by the Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology are eligible to transfer to a university (Article 58-2 of the School Education Act).
Certificate of Completion: Two or more year advanced course, upper division, secondary education school
・While the duration of study for the advanced course at the upper division of a secondary education school is at least one year, those who complete two or more years and meet the standards specified by the Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology are eligible to transfer to a university (Article 70 of the School Education Act).
Certificate of Completion: Two or more year advanced course, upper secondary department, school for special needs education
・While the duration of study for the advanced course in the upper secondary department at a school for special-needs education is at least one year, those who complete two or more years and meet additional criteria specified by the Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology are eligible to transfer to a university (Article 82 of the School Education Act).
Certificate of Completion: One year course, professional training colleges
・The requirements for completion of a professional training college program are enrollment for at least one year and, in principle, completion of 800 credit hours (one credit hour is 50 minutes) or acquisition of at least 30 credits in one year.
Certificate of Completion: One year advanced course, upper secondary school
・The duration of study for the advanced course at an upper secondary school is at least one year (Article 58, Paragraph 2 of the School Education Act).
Certificate of Completion: One year advanced course, upper division, secondary education school
・The duration of study for the advanced course in the upper division of a secondary education school is at least one year (Article 70 of the School Education Act).
Certificate of Completion: One year advanced course, upper secondary department, school for special needs education
・The duration of study for the advanced course in the upper secondary department at a school for special needs education is at least one year (Article 82 of the School Education Act).
Certificate of Graduation: Secondary education school
・Secondary school programs are classified into two categories: three-year lower term programs and three-year upper-term programs.
Certificate of Graduation: Upper secondary course, specialized training college
・While the duration of study in the upper secondary course at specialized training colleges is at least one year, those who have completed a three-year or longer upper secondary course at a specialized training college and meet additional criteria specified by the Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology are eligible for university admission.
Certificate of Completion: 3rd grade of regular course, college of technology (KOSEN)
・Colleges of Technology (KOSEN) are five-year higher education institutions that start at the upper secondary education (level 3). Students who complete the third year are eligible for university admission.
Certificate: Upper secondary school equivalency examination
・The examination is administered by the Japanese government to certify that an applicant has academic abilities equivalent to those of a high school graduate. Successful applicants receive a certificate and are eligible for university admission. Those above 16-year-olds can take the examination from the year they turn 16 years old, and if they pass all the subjects, they become successful applicants from the day after their 18th birthday.
Certificate of Graduation: Compulsory education school
・Compulsory education school programs are divided into elementary education (first six years) and lower secondary education (next three years).
Certificate: Lower secondary school equivalency examination
・Lower secondary school equivalency examination is administered by the Japanese government in accordance with Article 18 of the School Education Act to certify whether children, whose guardians have been exempted from the obligation to send them to compulsory education schools due to illness or other unavoidable reasons, have academic abilities equivalent to junior high school graduation. Successful applicants receive a certificate and are eligible to enter high school.
